Intelligent Third-Party Risk Management, Simplified
RiskImmune™ is a next-generation TPRM solution that helps organizations automate, monitor, and reduce third-party risks. Designed for simplicity and powered by cutting-edge AI, we take the complexity out, so you can focus on growth.
“Trusted by enterprises, including industry leaders in finance, healthcare, and tech.”
(4.7/5) from users worldwide.
We've Worked With Some Of The Biggest Brands




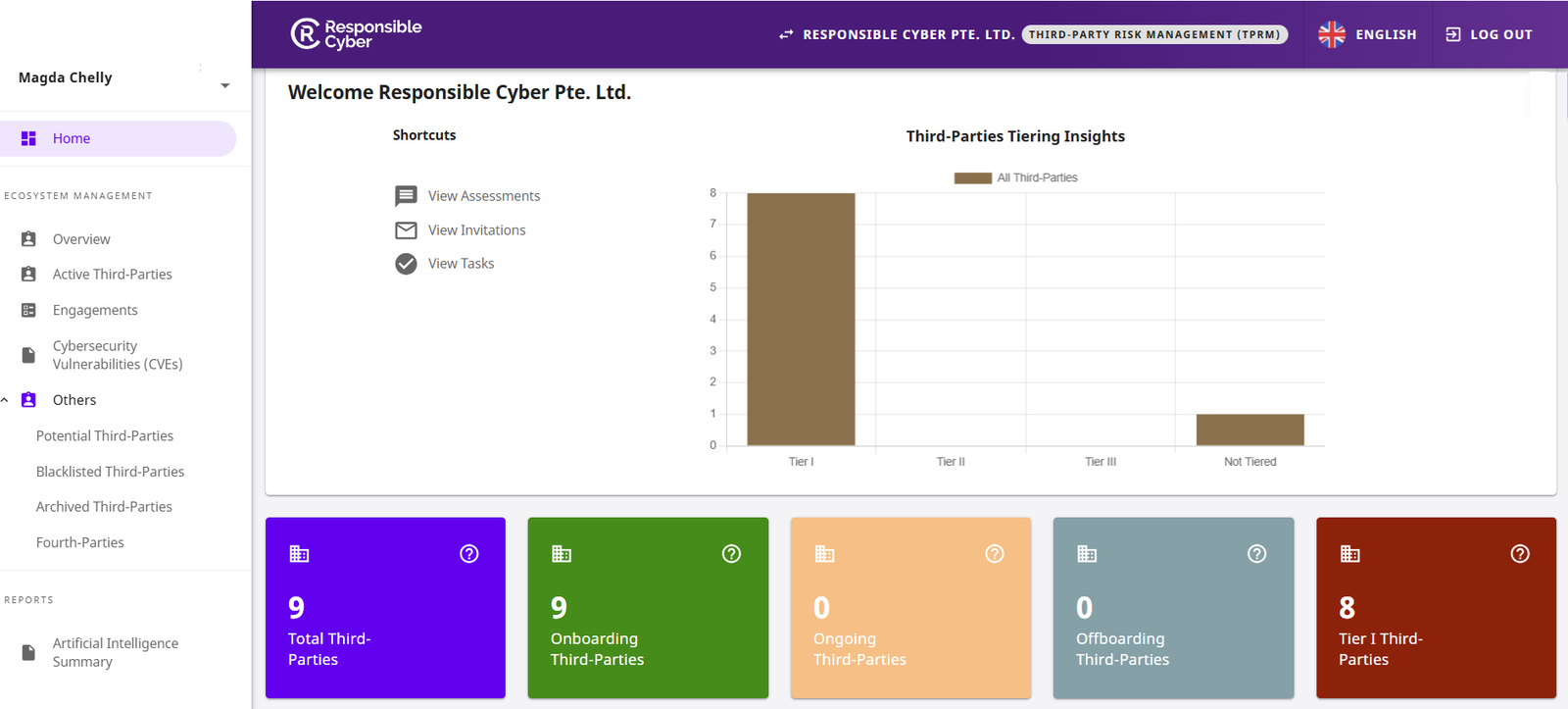
20,000
80
4
Quality Over Quantity
How RiskImmune™ Works?

“We believe in the tool’s added value benefits, and we are looking forward to building a long-term sustainable partnership and collaborating beyond Singapore.”
Andrew Taylor, Senior Vice President. Financial Lines Asia at MSIG Singapore
Featured Headlines
Technology
Frequently asked questions

How is RiskImmune™ different from SecurityScorecard or OneTrust?
RiskImmune™ goes beyond cybersecurity ratings. In addition to assessing vendor security posture, it provides comprehensive product, service, and project risk evaluations. This includes advanced assessments for technologies like IoT devices, APIs, and other critical infrastructure, ensuring you get a 360° view of potential risks.
Can RiskImmune™ evaluate non-technical vendor risks?
Absolutely! RiskImmune™ supports assessments for both technical and non-technical risks. Whether it’s a software vendor, a service provider, or even a product launch, our platform tailors risk assessments to fit your specific needs.
How does RiskImmune™ handle emerging technology risks like IoTs or APIs?
RiskImmune™ is designed to address cutting-edge technology risks. With specialized frameworks for IoTs, APIs, and other digital tools, you can identify vulnerabilities, ensure compliance, and minimize risk in adopting new tech.
Our founders have been featured in the biggest newspapers








